
While quantum entanglement usually refers to correlations between particles separated by distance, chronal entanglement proposes a correlation across time. In theory, the state of a particle at one point in time could be linked to the state of the same or another particle at a different time. This concept challenges the linear perception of time and has implications for quantum information theory and potentially for manipulating the temporal order of events.

Michio Kaku Explains Parallel Universes: Like Tuning Into Different Radio Stations
>
Renowned physicist Michio Kaku offers a fascinating analogy to explain the concept of parallel universes. According to Kaku, the multiverse isn’t just a theoretical abstraction but something you can picture like multiple radio stations broadcasting simultaneously. Each station represents a different universe, with its own unique version of reality.
pIn this analogy, you are “tuned” to just one frequency — your current universe — which means you only perceive one version of reality at a time. Other universes, potentially filled with entirely different events, such as dinosaurs roaming your living room or alien civilizations thriving nearby, exist but remain invisible because their frequencies don’t match your own.
pKaku’s idea helps us grasp how multiple realities could coexist without interacting directly. Each universe vibrates at a different frequency, so your consciousness aligns with one specific reality, while others remain parallel, unseen but real. This concept opens up profound questions about the nature of existence, reality, and what lies beyond our sensory perceptions.
While this theory is still in the realm of speculative physics, it offers an intriguing framework to explore the mysteries of the cosmos and the possibility of many “yous” living out different lives across countless universes.

An AI just discovered a new law of physics—without being told what physics is.
A team at Columbia University built a neural network and fed it raw video footage of swinging pendulums, rolling balls, and bouncing objects. The AI wasn’t given any equations. No Newton, no Einstein, no context. And yet, after analysing patterns for hours, it produced what researchers call “new coordinates of understanding”—entirely original variables.
These were not existing measurements like mass, speed, or time. Instead, they were unknown physical parameters, abstract and alien to our current models. When researchers reverse-engineered them, they found the AI had rediscovered classical mechanics—but using its own symbolic language.
This could be the beginning of a new way to study the universe: asking machines to describe reality as they see it. With no preconceptions. No human biases. Some of the variables even hinted at hidden symmetries physicists hadn’t noticed before—suggesting the AI might be uncovering deeper laws still beyond us.
It's a revolutionary shift. Instead of coding models into machines, we let them observe the universe like infants—learning not just our physics, but possibly better physics. The potential for breakthroughs in quantum gravity, dark matter, and cosmology is now enormous.
And that raises a haunting idea: what if the universe is ultimately more understandable to AI than to human minds?

Could consciousness be a quantum phenomenon? New research is exploring links between the brain and the universe.
Scientists are revisiting a bold idea: that human consciousness might come from quantum processes happening inside our brains – connecting our minds to the fabric of the universe.
This theory, known as Orch OR (Orchestrated Objective Reduction), was developed by physicist Roger Penrose and doctor Stuart Hameroff. They suggest that tiny structures in brain cells, called microtubules, may be able to hold quantum states – something once thought impossible in the brain’s warm, messy environment.
Recent experiments now show that these quantum effects might last longer than expected inside microtubules. That means the brain could be using the same strange rules that govern particles at the smallest scales—like superposition (being in multiple states at once) and entanglement (instant connection between particles, even across space).
Physicist Timothy Palmer has added another layer to the theory. He believes that consciousness might be linked to a higher-dimensional, fractal-like structure of the universe called the invariant set. In this model, the laws of physics – including quantum phenomena – are governed by a deeper geometric pattern, and consciousness might emerge from our position within this state space.
While none of this is confirmed, the research opens up exciting new ways of thinking about the mind. Rather than being just a product of brain chemistry, consciousness might be a deeper part of the universe – rooted in the laws of quantum physics.
The Pimacy Of Doubt

What if gravity isn’t just pulling stuff together—but streamlining cosmic code?
Physicist Melvin Vopson has dropped a theory that sounds straight out of The Matrix: the universe might be a giant computer, and gravity? Just an effect of it optimizing data.
He suggests that as particles behave like bits and spacetime acts like a cosmic hard drive, gravity works like a ZIP file—compressing and simplifying information across the universe.
This wild idea builds on “infodynamics,” where information is treated like physical stuff—with mass, space, and energy. So, when you look at a planet’s gravitational pull, you might actually be witnessing the universe trying to reduce data clutter.
Mind blown? Same. If this holds, it could rewrite how we see everything from quantum mechanics to dark matter.

This iconic image was captured by Voyager 1 on February 14, 1990, at the suggestion of Carl Sagan. As the spacecraft was leaving our planetary neighborhood and heading toward the edge of the Solar System, it turned around for one final glance at its home — Earth.
"Look again at that dot. That's here. That's home. That's us. On it everyone you love, everyone you know, everyone you ever heard of, every human being who ever was, lived out their lives. The aggregate of our joy and suffering, thousands of confident religions, ideologies, and economic doctrines, every hunter and forager, every hero and coward, every creator and destroyer of civilization, every king and peasant, every young couple in love, every mother and father, hopeful child, inventor and explorer, every teacher of morals, every corrupt politician, every "superstar", every "supreme leader", every saint and sinner in the history of our species lived there — on a mote of dust suspended in a sunbeam." — Carl Sagan, Pale Blue Dot, 1994 A Pale Blue Dot (Tribute to Carl Sagan)

Tiny black holes might be zipping through your furniture — and even your body — without a trace. Scientists say they could be all around us. Imagine a black hole so small it could be passing through your kitchen table and even your body.
That’s the stunning possibility proposed by cosmologists Dejan Stojkovic and De-Chang Dai in a recent study published in Physics of the Dark Universe. They suggest that tiny, dense entities called Primordial Black Holes (PBHs), which may have formed shortly after the Big Bang, could be zipping through Earth right now—possibly even getting trapped inside planets, moons, or asteroids. Unlike traditional black holes formed by dying stars, PBHs are hypothesized to originate from fluctuations in the dense early universe and might even be a source of the mysterious dark matter.
According to the researchers, these minuscule black holes could tunnel through solid matter, boring microscopic holes just 0.1 microns wide. In some scenarios, PBHs could become lodged in celestial bodies, slowly draining their liquid cores until they become hollow shells. Fortunately for us, even the densest PBH—estimated to weigh more than 20 quintillion pounds—would be moving so fast and interacting so weakly with human tissue that it wouldn’t cause harm. So while the idea of a black hole lurking in your living room may sound terrifying, the science says it’s more of a cosmic curiosity than a household hazard.

Quantum Touch:
You can never touch anything. Your atoms repel objects when they are 10⁻⁸ m away from you, you only feel the force of resistance. Technically right now you are hovering. No touch, No hugs, No kiss and no...... It's all you feel!
1. Atomic Repulsion
- At distances closer than ~10⁻⁸ meters (1 Ångström), electron clouds surrounding atoms generate strong repulsive electrostatic forces. - What we perceive as "touch" is actually electromagnetic repulsion, not direct particle contact.
2. Quantum Reality:
- Matter is mostly empty space. If an atom were the size of a stadium, its nucleus would be a grain of sand at the center. - "Solid" objects never truly intersect; their stability arises from quantum electromagnetic fields.
3. Philosohical Angle:
- While touch is fundamentally a force interaction, this does not diminish lived experience. Emotions, bonds, and physical sensations remain neurologically and biologically real.
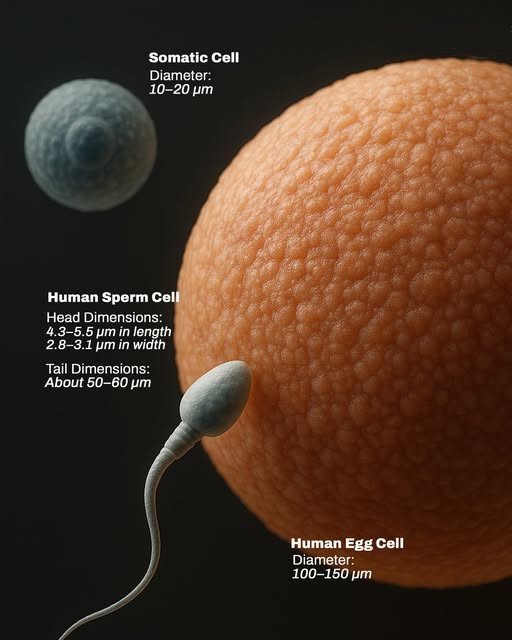
The human sperm cell is the smallest cell in the human body, while the human egg cell is the largest. Here's a relative size comparison between them, along with a typical somatic cell. A micrometer (μm) is a unit of length equal to one-millionth of a meter, or one-thousandth of a millimeter—so tiny that it's commonly used to measure cells, bacteria, and other microscopic structures. To put it into perspective, a single human hair is about 70 to 100 micrometers wide. A sperm cell measures about 4.3 to 5.5 micrometers in diameter, making it roughly 1/20th the size of an egg cell; a typical somatic cell ranges from 10 to 20 micrometers, or about 1/10th the size—while the egg cell, at 100 to 150 micrometers, serves as the reference for this comparison.
Why will this June's Full Moon barely rise in the sky for millions of people? What ancient cycle is behind this rare event? And why does the Moon vanish completely in parts of the world? This video unpacks the hidden mechanics behind one of the Moon’s most dramatic movements in decades. Watch to see what makes the June 2025 Full Moon so different.


